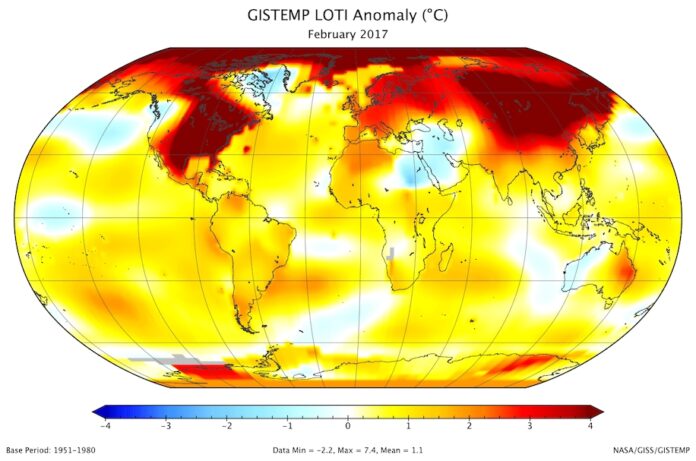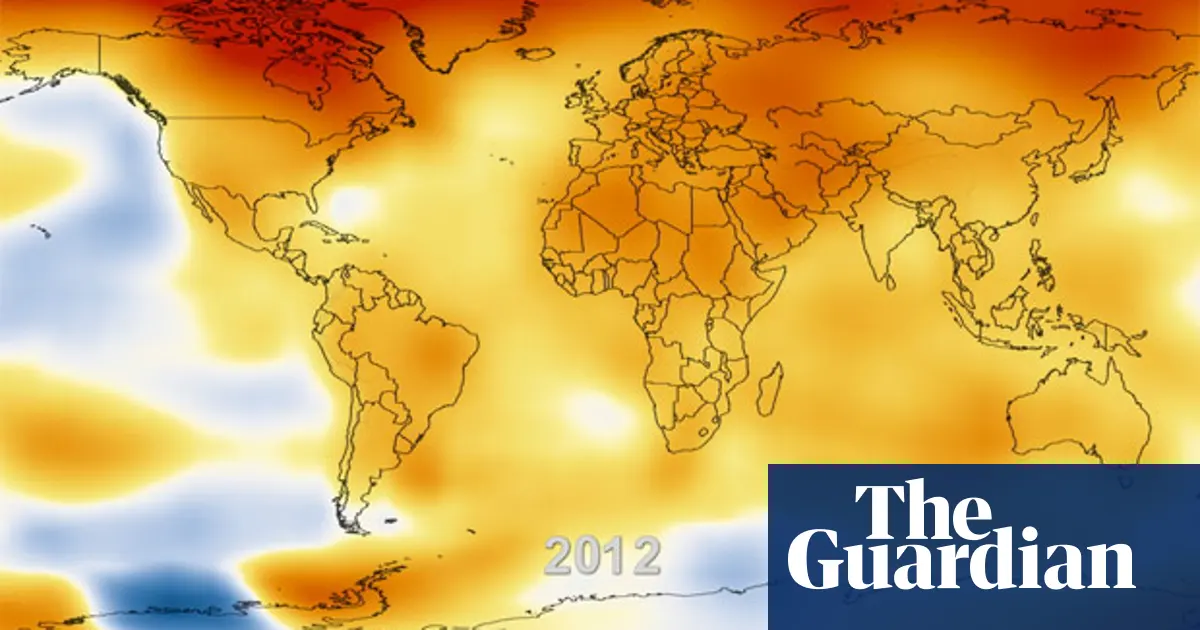
The Earth is on the brink of experiencing unprecedented global temperatures, a stark reminder of the urgent need for comprehensive climate action. As we continue to pump greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, the planet’s ability to regulate its climate is diminishing, leading to record-breaking heatwaves, melting ice caps, and rising sea levels. This article explores the factors driving these temperature increases, the consequences of inaction, and the necessary steps to mitigate this looming crisis.
Understanding the Causes of Rising Global Temperatures
The primary driver of rising global temperatures is the increase in greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O). These gases trap heat in the atmosphere, creating a “greenhouse effect” that leads to global warming. Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels for energy, deforestation, and industrial processes, are the main sources of these emissions.
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
CO2 is the most significant greenhouse gas emitted by human activities, accounting for about 76% of global greenhouse gas emissions. It primarily comes from burning fossil fuels for electricity, heat, and transportation. Deforestation also contributes significantly, as trees that absorb CO2 are removed, releasing stored carbon into the atmosphere.
Methane (CH4)
Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, with a global warming potential 28-36 times greater than CO2 over 100 years. It is released during the production and transport of coal, oil, and natural gas, as well as from livestock and other agricultural practices.
Nitrous Oxide (N2O)
N2O has a global warming potential about 298 times that of CO2 over a 100-year period. It is mainly emitted from agricultural and industrial activities, as well as during the combustion of fossil fuels and biomass.
Consequences of Rising Temperatures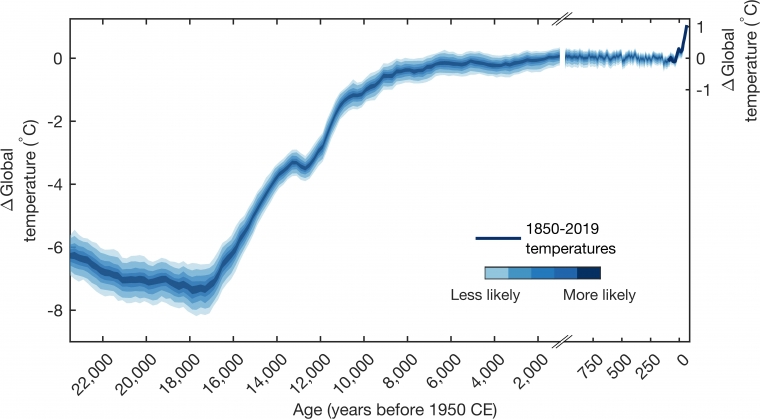
The impacts of rising global temperatures are far-reaching and potentially catastrophic. They include more frequent and severe heatwaves, changes in precipitation patterns, stronger and more destructive storms, and a rise in sea levels. These changes threaten human health, agriculture, water supply, and biodiversity.
Health Impacts
Extreme heat can lead to heatstroke, dehydration, and respiratory issues, particularly among vulnerable populations such as the elderly, children, and those with pre-existing health conditions. The spread of vector-borne diseases, such as malaria and dengue fever, is also expected to increase as warmer temperatures expand the habitats of disease-carrying insects.
Agricultural and Food Security
Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can disrupt agricultural production, leading to food shortages and higher prices. Crops that are sensitive to temperature changes, such as wheat and maize, may see reduced yields. Additionally, the frequency of extreme weather events can destroy crops and reduce the reliability of food supplies.
Water Supply
As temperatures rise, so does the rate of evaporation, reducing water availability in many regions. Glaciers and snowpacks, which provide water for millions of people, are melting at unprecedented rates. This reduction in freshwater availability can lead to conflicts over water resources, particularly in already arid regions.
Biodiversity and Ecosystems
Rising temperatures can alter the habitats and migration patterns of many species, leading to a loss of biodiversity. Coral reefs, which are particularly sensitive to temperature changes, are experiencing widespread bleaching and die-offs. The disruption of ecosystems can have cascading effects, impacting not just wildlife, but also the human communities that depend on these ecosystems for their livelihoods.
Urgent Climate Actions Needed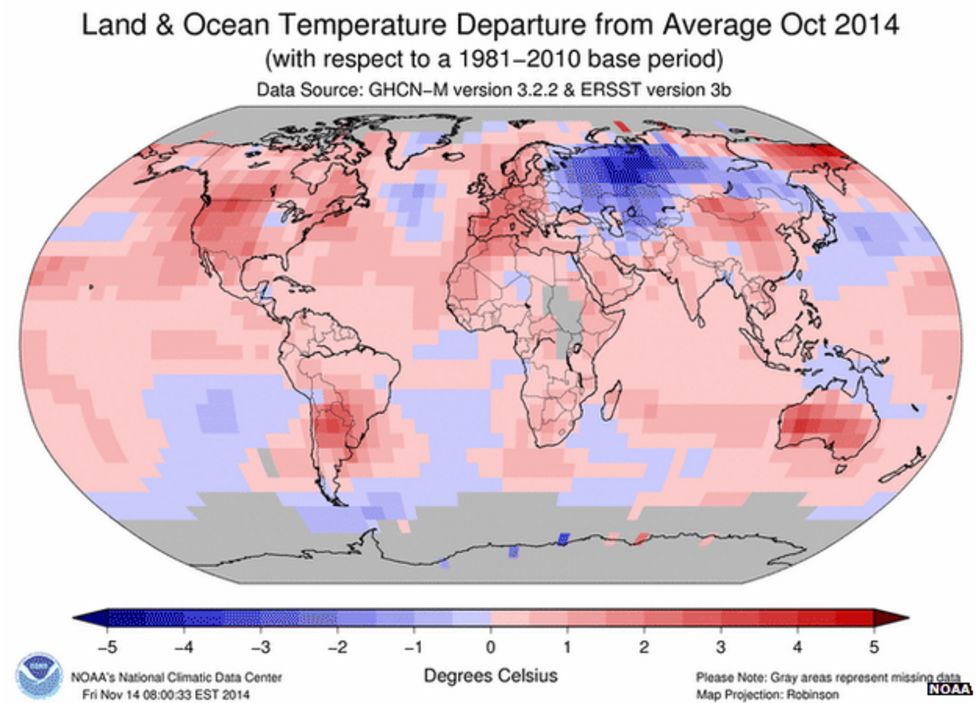
To avoid the worst impacts of climate change, urgent and comprehensive action is needed on a global scale. This involves reducing greenhouse gas emissions, transitioning to renewable energy sources, enhancing energy efficiency, and protecting and restoring forests.
Reducing Emissions
Countries need to commit to and achieve significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions. This can be done through policies that promote the use of renewable energy, such as solar and wind power, and through regulations that limit emissions from industrial sources.
Transitioning to Renewable Energy
Transitioning to renewable energy sources is crucial for reducing emissions. Governments and private sectors should invest in the development and deployment of renewable energy technologies. This includes not only solar and wind power but also other sources like hydroelectric and geothermal energy.
Enhancing Energy Efficiency
Improving energy efficiency in buildings, transportation, and industries can significantly reduce emissions. This can be achieved through the adoption of energy-efficient technologies and practices, such as LED lighting, energy-efficient appliances, and electric vehicles.
Protecting and Restoring Forests
Forests play a critical role in absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere. Protecting existing forests and restoring degraded ones can help mitigate climate change. Reforestation and afforestation efforts should be prioritized, and policies that promote sustainable land use should be implemented.
Global Cooperation and Policy Implementation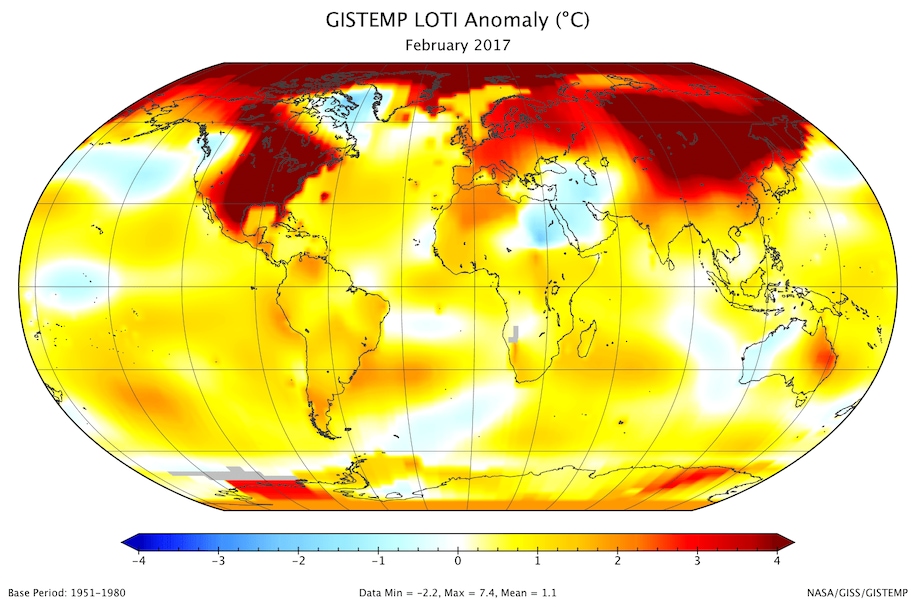
Climate change is a global issue that requires international cooperation. Countries must work together to develop and implement policies that address the root causes of climate change. The Paris Agreement, which aims to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius, is a critical framework for this cooperation.
Conclusion
The evidence is clear: global temperatures are set to break new records, and urgent climate action is needed to prevent catastrophic consequences. By reducing emissions, transitioning to renewable energy, enhancing energy efficiency, and protecting forests, we can mitigate the impacts of climate change and ensure a sustainable future for generations to come. The time for action is now, and it requires a collective effort from governments, businesses, and individuals worldwide.