Introduction
Jupiter, the largest planet in our Solar System, is home to a fascinating array of moons, but none are as intriguing as Europa. With its icy surface and potential subsurface ocean, Europa has captured the imagination of scientists and space enthusiasts alike. NASA’s Europa Clipper mission, set to launch in the coming years, aims to unlock the mysteries of this enigmatic moon. In this article, we’ll explore the mission’s objectives, technological innovations, and the significance of Europa in our quest to understand the potential for life beyond Earth.
The Allure of Europa
Europa, one of Jupiter’s four largest moons, was first observed by Galileo Galilei in 1610. What makes Europa particularly captivating is its smooth, icy surface, which hints at a subsurface ocean beneath. This ocean, if confirmed, could contain more than twice the amount of water found on Earth, making Europa a prime candidate in the search for extraterrestrial life.
The surface of Europa is covered with a thick layer of ice, estimated to be around 15 to 25 kilometers (10 to 15 miles) deep. Beneath this icy crust, scientists believe there exists a global ocean of liquid water, kept warm by tidal forces generated by Jupiter’s massive gravitational pull. This ocean may interact with Europa’s rocky mantle, creating conditions that could potentially support life.
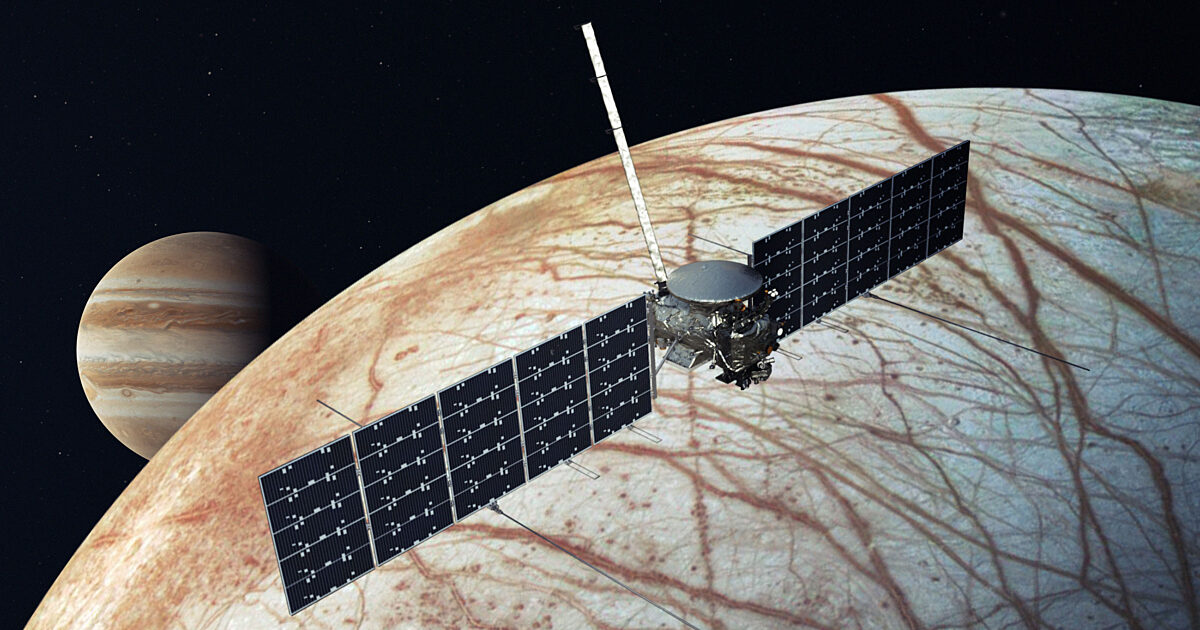
NASA’s Europa Clipper Mission
NASA’s Europa Clipper mission is designed to investigate the habitability of Europa by conducting detailed reconnaissance of its ice-covered ocean. Scheduled for launch in the 2020s, this mission will be equipped with an array of scientific instruments to analyze Europa’s surface and subsurface.
Mission Objectives
- Surface Composition Analysis: One of the primary goals is to analyze the surface composition of Europa to understand its ice structure and the presence of potential chemical ingredients necessary for life. Instruments like the Near Infrared Mapping Spectrometer (NIMS) will provide detailed spectra of the surface, identifying the chemical makeup and mapping the distribution of different compounds.
- Subsurface Ocean Exploration: The Clipper will use radar to penetrate Europa’s icy crust and assess the depth and characteristics of the subsurface ocean. The Ice-Penetrating Radar (IPR) will provide insights into the ice’s thickness and the ocean’s properties.
- Geological Activity Monitoring: Europa’s surface is crisscrossed with ridges and grooves, suggesting significant geological activity. The mission aims to study these features to determine whether there are any active processes that could influence the ocean below.
- Magnetic Field Study: Europa’s interaction with Jupiter’s magnetic field will be investigated to understand the ocean’s conductivity. The Magnetometer instrument will measure variations in the magnetic field, which can indicate the presence of a salty, conductive ocean beneath the ice.
- Atmospheric Analysis: The Europa Clipper will also examine the tenuous atmosphere of Europa, which consists mainly of oxygen. Understanding the atmosphere will help scientists determine how materials are exchanged between the surface and the subsurface ocean.
Technological Innovations
The Europa Clipper mission incorporates several cutting-edge technologies to ensure its success:
- Advanced Propulsion System: To reach Jupiter, the spacecraft will use a highly efficient propulsion system, allowing it to perform multiple flybys of Europa while minimizing travel time and fuel consumption.
- High-Resolution Imaging: Equipped with high-resolution cameras, the Clipper will capture detailed images of Europa’s surface, enabling scientists to study surface features and potential landing sites for future missions.
- Radiation Shielding: Jupiter’s intense radiation environment poses a significant challenge for spacecraft. The Europa Clipper will be shielded with advanced materials to protect its instruments and ensure data integrity.
Significance of the Mission
The Europa Clipper mission represents a critical step in our quest to find life beyond Earth. By exploring Europa’s icy surface and subsurface ocean, scientists hope to answer fundamental questions about the potential for life in the Solar System. The data gathered will also inform future missions, including potential landers or even sample-return missions.
Understanding Europa’s habitability could have profound implications for our knowledge of life’s potential in the universe. If Europa’s subsurface ocean contains the right conditions, it might offer clues about how life could arise in similar environments elsewhere in the cosmos.
Conclusion
NASA’s Europa Clipper mission is poised to revolutionize our understanding of Jupiter’s icy moon and its potential to harbor life. With its advanced technologies and comprehensive scientific objectives, the mission will provide unprecedented insights into Europa’s composition, geology, and habitability. As we stand on the brink of this exciting exploration, the quest to uncover the secrets of Europa promises to expand our knowledge of the Solar System and the potential for life beyond our planet.