Introduction
Neurology is witnessing a transformative era, driven by groundbreaking research into Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. These neurodegenerative disorders have long posed significant challenges for both patients and researchers. However, recent advancements are paving the way for innovative treatments and a deeper understanding of these complex conditions. This article explores the latest research breakthroughs and their potential to revolutionize neurology, offering hope for millions worldwide.
Understanding Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases
Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common form of dementia, characterized by progressive memory loss, cognitive decline, and behavioral changes. It primarily affects older adults and has no known cure. Research has identified several key factors contributing to Alzheimer’s, including the accumulation of beta-amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain, which disrupt neural communication and lead to cognitive decline.
Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects movement control. It is characterized by tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia (slowness of movement). The disease results from the loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain. While not as widely studied as Alzheimer’s, recent research is shedding light on its underlying mechanisms and potential therapies.
Cutting-Edge Research in Alzheimer’s Disease
1. Early Detection and Diagnosis
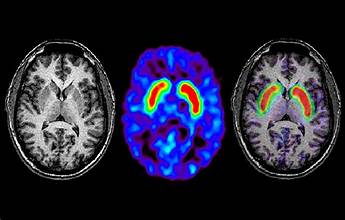
One of the most promising areas of research is the development of early diagnostic tools. Recent studies have focused on identifying biomarkers in blood and cerebrospinal fluid that could indicate the onset of Alzheimer’s disease before symptoms appear. Advanced imaging techniques, such as PET scans with amyloid tracers, are also being refined to detect the disease in its earliest stages.
2. Targeting Beta-Amyloid and Tau Proteins
Research into beta-amyloid plaques and tau tangles remains a central focus. Novel therapeutic approaches are being developed to target these proteins and prevent their accumulation. Monoclonal antibodies, such as aducanumab and lecanemab, have shown promise in clinical trials by reducing amyloid plaques and potentially slowing cognitive decline.
3. Gene Therapy and Precision Medicine
Gene therapy offers the potential to address genetic risk factors associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Scientists are exploring ways to modify genes associated with the disease, such as the APOE gene, which influences amyloid plaque formation. Precision medicine, which tailors treatments based on an individual’s genetic profile, is also gaining traction as a way to personalize Alzheimer’s care.
Cutting-Edge Research in Parkinson’s Disease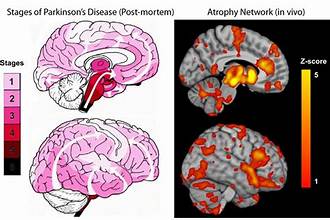
1. Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy is emerging as a revolutionary approach for Parkinson’s disease. Researchers are investigating the use of stem cells to replace lost dopamine-producing neurons. Clinical trials involving the transplantation of stem cells derived from various sources, including embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells, are underway to assess their efficacy and safety.
2. Neuroprotective Agents
Another exciting area of research involves identifying neuroprotective agents that could slow or halt the progression of Parkinson’s disease. Compounds such as rasagiline and safinamide are being studied for their potential to protect neurons from damage and improve motor symptoms.
3. Genetic and Environmental Factors
Understanding the interplay between genetic and environmental factors in Parkinson’s disease is crucial for developing effective treatments. Researchers are investigating how genetic mutations, such as those in the SNCA and LRRK2 genes, interact with environmental toxins to trigger disease onset. This research could lead to targeted interventions that address specific risk factors.
Future Directions in Neurology Research
1. Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine is set to play a significant role in the future of neurology. By integrating genetic, molecular, and clinical data, researchers aim to develop tailored treatment plans that address the unique characteristics of each patient’s condition.
2. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are revolutionizing research by enabling more accurate predictions and analyses of complex data. AI algorithms are being used to identify potential biomarkers, predict disease progression, and optimize treatment strategies for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases.
3. Collaboration and Data Sharing
Collaboration among researchers, institutions, and pharmaceutical companies is essential for advancing neurology research. Data sharing initiatives and global research networks are fostering collaboration and accelerating the development of new therapies.
Conclusion
The field of neurology is undergoing a remarkable transformation, driven by cutting-edge research in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. From early detection and innovative therapies to personalized medicine and advanced technologies, these advancements hold the promise of revolutionizing our approach to neurodegenerative disorders. As research continues to evolve, the hope for effective treatments and a deeper understanding of these complex conditions grows stronger, offering renewed hope for patients and their families.









